IRS 1040-A 2017-2026 free printable template
Instructions and Help about IRS 1040-A
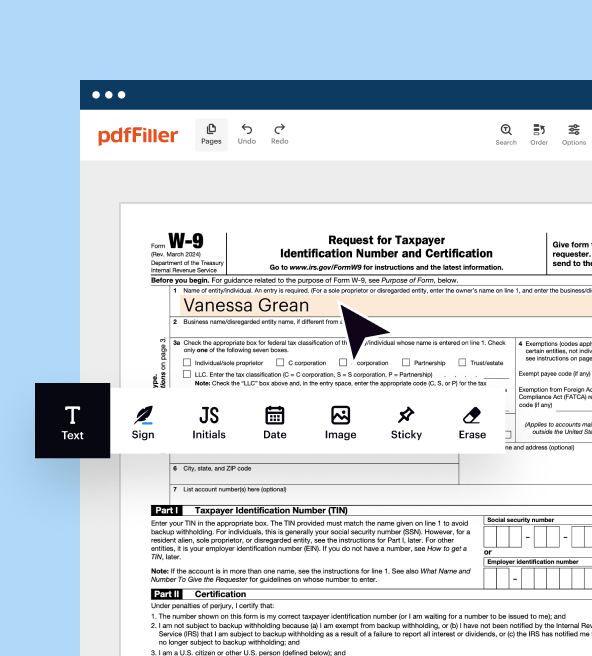
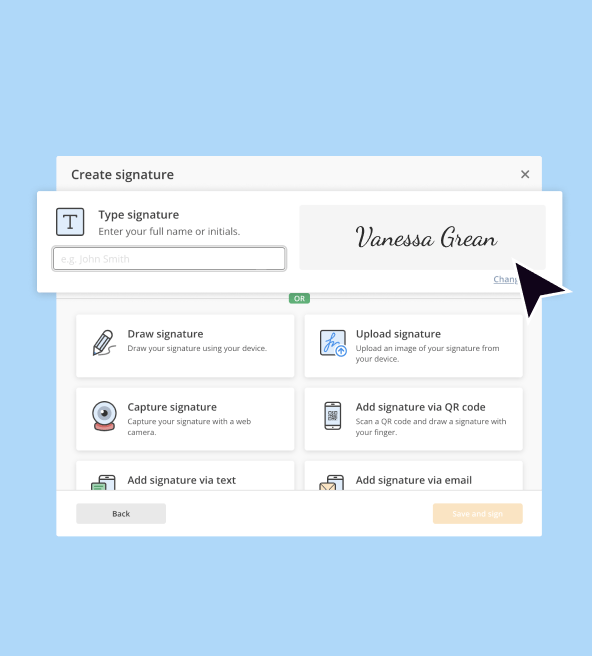
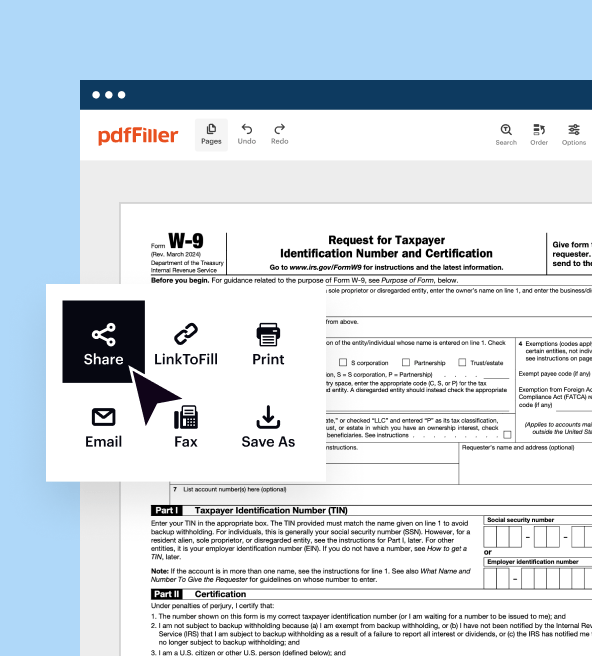
How to edit IRS 1040-A
How to fill out IRS 1040-A
Latest updates to IRS 1040-A
All You Need to Know About IRS 1040-A
What is IRS 1040-A?
Who needs the form?
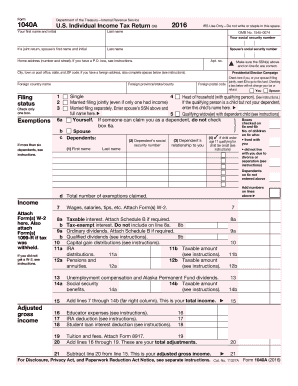
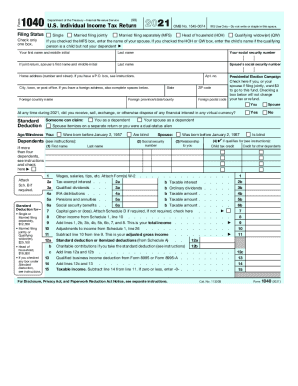
Components of the form
What information do you need when you file the form?
Where do I send the form?
What is the purpose of this form?
When am I exempt from filling out this form?
Due date
What are the penalties for not issuing the form?
Is the form accompanied by other forms?
FAQ about IRS 1040-A
What should I do if I made a mistake on my IRS 1040-A?
If you realize that you've made a mistake on your IRS 1040-A, you need to file an amended tax return using Form 1040-X. It's essential to address any discrepancies to avoid issues with the IRS. Ensure you include any supporting documentation and corrections to accurately reflect your financial situation.
How can I track the status of my IRS 1040-A after filing?
To track the status of your IRS 1040-A, you can use the 'Where's My Refund?' tool available on the IRS website. This tool will inform you about the processing status and any refund details. Be ready to provide your filing status and other identifying details to access your information.
What should I know about the privacy and data security of my IRS 1040-A information?
When filing your IRS 1040-A, it's crucial to understand that the IRS maintains strict privacy and data security protocols. They use various measures to secure your personal information against unauthorized access. Additionally, retaining copies of your return securely is essential for protecting your financial data.
Are there common errors I should watch for when submitting my IRS 1040-A?
Common errors when filing the IRS 1040-A include incorrect Social Security numbers, miscalculations of tax liabilities, and failing to sign the form. It's beneficial to double-check all entries and ensure that you've used the most current tax year resources to mitigate mistakes that could delay processing.
What should I do if I receive a notice from the IRS after filing my 1040-A?
If you receive a notice from the IRS after filing your IRS 1040-A, carefully read the correspondence to understand its purpose. It's important to respond promptly if action is required, providing any necessary documentation to clarify or resolve the issue indicated in the notice. Keep a record of your communication for future reference.
See what our users say